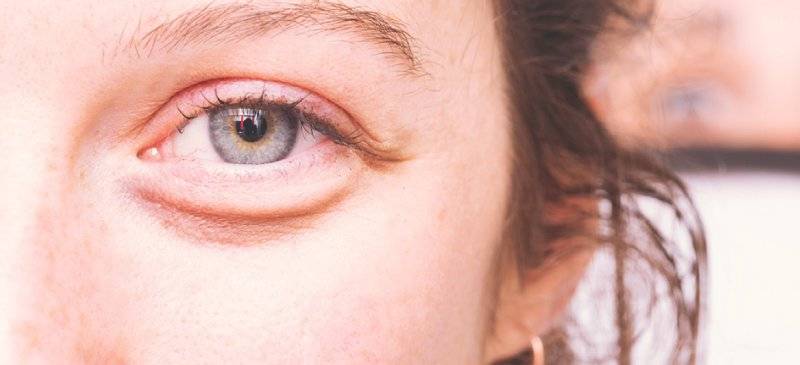
Bags under the eyes — mild swelling or puffiness under the eyes — are common as you age. With ageing, the tissues around your eyes, including some of the muscles supporting your eyelids, weaken. Normal fat that helps support the eyes can then move into the lower eyelids, causing the lids to appear puffy. Fluid also may accumulate in the space below your eyes, adding to the swelling.
Bags under the eyes are usually a cosmetic concern and rarely a sign of a serious underlying medical condition. At-home remedies, such as cool compresses, can help improve the appearance of bags under the eyes. For persistent or bothersome under-eye puffiness, eyelid surgery may be an option.
Symptoms
Bags under eyes can include:
- Mild swelling
- Saggy or loose skin
- Dark circles
When to see a doctor
You may not like the way they look, but bags under eyes are usually harmless and don’t require medical care. See your doctor if the swelling is severe, persistent, painful, itchy or red.
Your doctor will want to rule out other possible causes that can contribute to the swelling, such as thyroid disease, infection or an allergy. He or she may refer you to a doctor who specializes in the eyes (ophthalmologist).
Causes
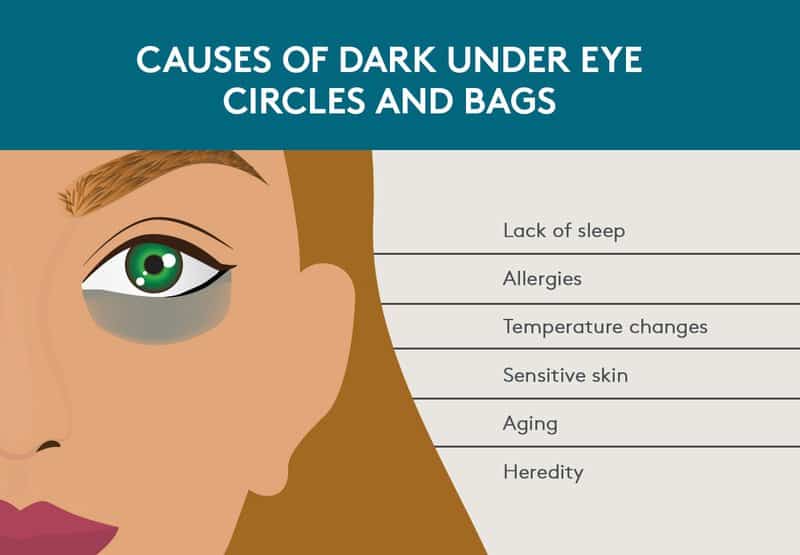
As you age, the tissue structures and muscles supporting your eyelids weaken. The skin may start to sag, and fat that is normally confined to the area around the eye (orbit) can move into the area below your eyes. Also, the space below your eyes can accumulate fluid, making the under-eye area appear puffy or swollen. Several factors cause or worsen this effect, including:
- Fluid retention, especially upon waking or after a salty meal
- Lack of sleep
- Allergies
- Smoking
- Heredity — under-eye bags can run in families
- Aging
- Temperature Changes
Treatment
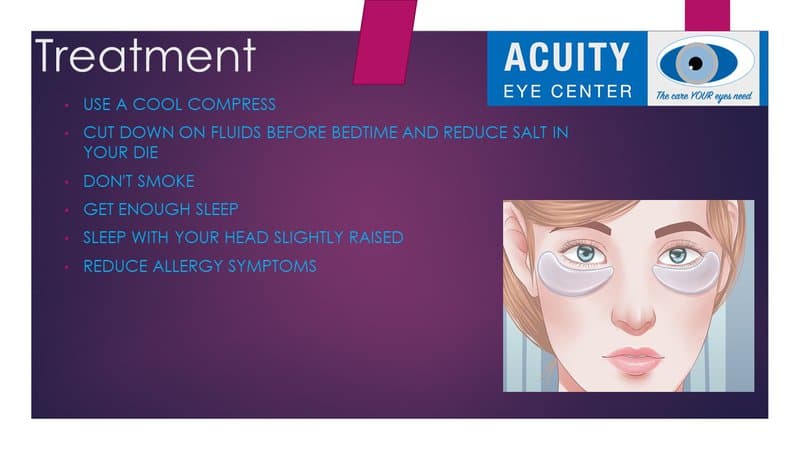
The following tips can help you reduce or eliminate bags under eyes:
- Use a cool compress. Wet a clean washcloth with cool water. While sitting up, apply the damp washcloth to the skin under and around your eyes for a few minutes using mild pressure.
- Cut down on fluids before bedtime and reduce salt in your diet. This will reduce the fluid retention that can cause bags under eyes.
- Don’t smoke. Smoking can aggravate the problem of bags under your eyes.
- Get enough sleep. For most adults, seven to nine hours is a good amount of sleep.
- Sleep with your head slightly raised. It may help to add an extra pillow or prop up the head of your mattress. Or elevate the entire head of the bed a few inches. This helps prevent fluid from accumulating around your eyes as you sleep. Dark circles caused by fluid retention in your lower eyelids usually go away when you get up.
- Reduce allergy symptoms. Avoid allergens when possible. Try over-the-counter allergy medications. Talk to your doctor about prevention strategies if you develop under-